
Tipsy
 |
 |
|
Tipsy |
 N-Body Home N-Body Home |
 About Us About Us |
 Search Search |
 Contact Info Contact Info |
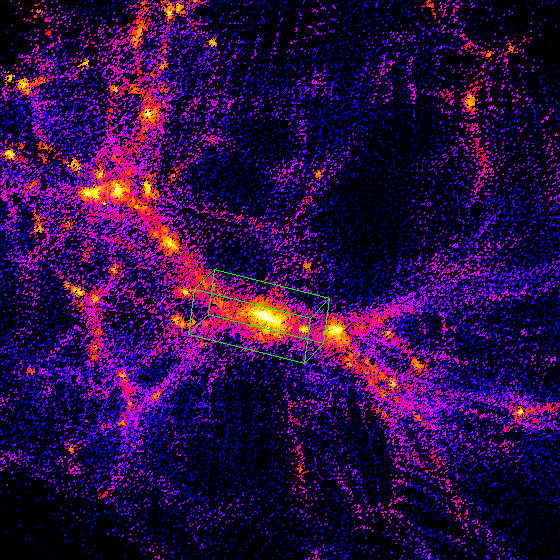
Visit the TIPSY picture gallery.
For online descriptions of (some of) the TIPSY commands see the man pages
The developement of TIPSY was motivated by the need to quickly display and analyze the results of N-body simulations. Most data visualization packages are designed for the display of gridded data, and hence are unsuitable for use with particle data. Therefore, a special package was built that could easily perform the following functions:
The basic data structure is an array of particle structures. Since TIPSY was built for use with cosmological N-body simulations, there are actually three separate arrays for each of the types of particle used in such simulations: collisionless particles, SPH particles, and star particles. A single timestep is read into these arrays from a disk file. Display is done by finding the x and y coordinates of the particles in the rotated coordinate system, and storing them in arrays. Screen coordinates are calculated from these arrays according to the current zoom factor. Also, a software Z-buffer is maintained to save time if many particles project to the same screen pixel. There are several types of display. An ``all plot'' displays all particles colored according to their type. A ``radial plot'' will color particles according to the projection of the velocity along the line-of-sight. A ``gas plot'' will color gas according to SPH quantities such as density, temperature, neutral hydrogen fraction, etc. Subsets of particles are maintained using ``boxes''. A box structure contains a bounding box, and an array of pointers to particles within the box. All display and analysis functions are performed on the ``active box''. By default all particles are loaded into box 0, which becomes the active box. If a new timestep is read from disk, all boxes are destroyed. A selection of particles can be followed between timesteps via a ``mark'' array. Marked particles are displayed in a different color, and the analysis functions can be told to only operate on the marked particles.
To obtain TIPSY, get the tar file from our Anonymous ftp-site at ftp-hpcc.astro.washington.edu. The relevant tar file is /pub/hpcc/tipsy.tar.gz. The script in /pub/hpcc/unpackage_tipsy will extract the tar file. Also see /pub/hpcc/tipsy_tools.tar.gz for code that reads and writes the tipsy binary file format.
To build tipsy, change into the code directory, and type configure. This should create a Makefile appropriate for your system. Then type make to build the TIPSY binary. The man directory contains preliminary man pages for the TIPSY commands.
For more information on TIPSY please send mail to the user mailing list, tipsy@u.washington.edu.
|
N-Body Shop University of Washington Box 351580 Seattle, WA 98195-1580 (206) 543-2888 voice, (206) 685-0403 FAX [comments to webmaster@www-hppc.astro.washington.edu] | |